
Ectopic Pregnancy in Vileparle, Mumbai
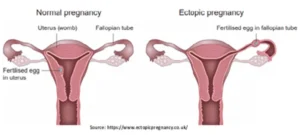
Pregnancy necessitates several steps in a woman’s body, from fertilization to delivery. One of these steps includes carrying a fertilized egg to the uterus to attach itself to the uterine wall. When a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, mainly in the fallopian tube, it is called an ectopic pregnancy.
In more than 90% of ectopic pregnancy cases, the fertilized egg implants in a fallopian tube. This is termed a tubal pregnancy. An ectopic pregnancy can occur on an ovary or in the abdominal cavity in rare cases.
The fertilized egg cannot develop properly outside of the uterus. The fallopian tube is not designed to hold a developing embryo and cannot stretch like the uterus. An ectopic pregnancy cannot be carried to term (until birth) and can be dangerous to the mother if not treated promptly.
Untreated ectopic pregnancy can result in life-threatening bleeding and necessitates immediate medical attention. Prompt treatment lowers your risk of ectopic pregnancy complications, increases your chances of future healthy pregnancies, and reduces future health complications.
Dr. Shweta Shah has extensive skills and 10+ years of experience dealing with gynecology and obstetrics complications such as ectopic pregnancy in Vileparle, Mumbai. She is also skilled in laparoscopic, hysteroscopic, and other gynecological procedures.
She has earned her patients’ respect and faith because of her exceptional expertise in managing infertility, high-risk pregnancies, endometriosis, PCOD cases, and other related issues. As a result, she is regarded as one of the best gynecologist and obstetrician in Vileparle, Mumbai.
In this article, we will discuss symptoms and causes and the diagnosis and treatment of ectopic pregnancy in Vileparle, Mumbai.
CONTACT US FOR MORE INFORMATION OR BOOK AN APPOINTMENT
Signs and Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy
Most ectopic pregnancies occur during the first few weeks of gestation. You may not even realize you are pregnant and may not notice any symptoms.
Early signs of an ectopic pregnancy may include:
- Light vaginal bleeding and pelvic pain.
- Stomach upset and vomiting.
- Severe abdominal cramps.
- Suffering from pain on one side of the body.
- Feeling dizzy or weak.
- Shoulder, neck, or rectum pain.
Your fallopian tube may burst or rupture due to an ectopic pregnancy. Severe pain, with or without severe bleeding, is one of the emergency symptoms. Call your doctor if you have heavy vaginal bleeding, lightheadedness, fainting, shoulder pain, or severe abdominal pain, especially on one side.
Now, let’s know the,
Causes and Risk Factors of Ectopic Pregnancy
You might never find out why you had an ectopic pregnancy. However, a damaged fallopian tube could be one of the causes. It may prevent the fertilized egg from entering your uterus.
The following conditions or risk factors may increase your chances of having an ectopic pregnancy:
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
- Smoking.
- Age more than 35 years.
- Sexually transmitted infection.
- Fallopian tube blockage as a result of an infection or inflammation.
- Endometriosis is a condition in which the uterine lining cells implant and grow elsewhere in the body.
- Scarring from pelvic surgery.
- Previous ectopic pregnancy.
- Birth defects that caused the tube to change shape.
- Tubal ligation (tying the tubes) or tubal ligation reversal.
- Use fertility drugs.
- Undergone fertility treatments, such as IVF.
An ectopic pregnancy can happen if you get pregnant while you have an intrauterine device (IUD) for birth control.
CONTACT US FOR MORE INFORMATION OR BOOK AN APPOINTMENT
Diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
A pelvic exam can assist your doctor in locating areas of pain, tenderness, or a mass in the fallopian tube or ovary. However, your doctor cannot diagnose an ectopic pregnancy simply by examining you. You will need some more tests, such as:
- Pregnancy test: Your doctor will recommend a human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) blood test to confirm your pregnancy. During pregnancy, the levels of this hormone rise. Your doctor may order a blood test every few days until an ultrasound can confirm or rule out an ectopic pregnancy, which usually occurs five to six weeks after conception.
- Ultrasound: Your doctor can see the exact location of your pregnancy with a transvaginal ultrasound. During this procedure, the doctor inserts a wand-like device into your vagina. Using sound waves, it creates images of your uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes and sends them to a nearby monitor. Abdominal ultrasound involves moving an ultrasound wand over your belly. Your doctor can employ this test to confirm your pregnancy or check for internal bleeding.
- Additional blood tests: Your doctor may order a complete blood count to check for anemia or other signs of blood loss. If you have an ectopic pregnancy, your doctor may also order blood tests to determine your blood type if you need a transfusion.
CONTACT US FOR MORE INFORMATION OR BOOK AN APPOINTMENT
Treatment of Ectopic Pregnancy
Because a fertilized egg cannot survive outside of the uterus, your doctor will need to remove it to prevent serious health problems.
Dr. Shweta Shah, one of the best female gynecologists in Vileparle, Mumbai, will employ two approaches, i.e., medications or surgical procedures, to treat ectopic pregnancy.
- Medication: An early ectopic pregnancy without severe bleeding is usually treated with methotrexate, a medication that inhibits cell growth and dissolves existing cells. The doctor administers the drug via an injection. Before receiving this treatment, the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy must be certain. Following the injection, your doctor may order another HCG test to see how well the treatment works and if you require additional medication.
- Surgical treatment
Two laparoscopic surgeries used to treat ectopic pregnancies are salpingostomy and salpingectomy. For these procedures, the surgeon makes a small incision near the navel in the abdomen. Then, the doctor views the tubal area using a thin tube equipped with a camera lens and light (laparoscope).
The surgeon removes the ectopic pregnancy during a salpingostomy, and the tube is left to heal on its own. Whereas the ectopic pregnancy and the tube are both removed during a salpingectomy.
The procedure you have depends on the amount of bleeding and damage and whether or not the tube has ruptured. Another consideration is whether your other fallopian tube is normal or shows signs of previous damage.
2. Emergency surgery
If you have severe bleeding or your doctor suspects a ruptured fallopian tube, you may require emergency surgery with a larger incision. This is known as a laparotomy. The fallopian tube can be saved in some cases. On the other hand, doctors often remove a ruptured tube.
Why Choose Dr. Shweta Shah?
- Personalized care tailored to individual needs
- Experienced and dedicated team of professionals
- Commitment to staying updated with the latest advancements in women’s health
- Comprehensive services ranging from routine check-ups to complex procedures
- Supportive and understanding environment
- Emphasis on open communication and building lasting relationships
- Prioritizing patient comfort, well-being, and satisfaction

Frequently Asked Questions
How long does recovery from ectopic pregnancy surgery take?
Most women can leave the hospital within a few days of surgery, though full recovery can take 5 to 7 weeks.
How long should I wait after an ectopic pregnancy before trying to conceive again?
After being treated for an ectopic pregnancy, you should consult your doctor about future pregnancies. Although pregnancy can occur soon after treatment, it is usually best to wait for three months. This gives your fallopian tube time to heal and reduces the risk of future ectopic pregnancies.
Can I conceive again after an ectopic pregnancy?
Most women who have had an ectopic pregnancy can have subsequent successful pregnancies. Following an ectopic pregnancy, you are more likely to have another.
It is critical to speak with your doctor about the causes of your ectopic pregnancy and any risk factors you may have that could lead to another ectopic pregnancy in the future.
Can an ectopic pregnancy be prevented?
No, you cannot prevent an ectopic pregnancy. However, you can try to reduce your risk factors by adopting a healthy lifestyle. These can include quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, and avoiding sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Before attempting to conceive, consult with your healthcare provider about any risk factors, you may have.
How early is an ectopic pregnancy detected?
Ectopic pregnancy is usually discovered in the early weeks of pregnancy. Most cases are detected during the first trimester (the first three months). It is generally detectable by the eighth week of pregnancy.
CONTACT US FOR MORE INFORMATION OR BOOK AN APPOINTMENT
Patients Review
What our patients say about us
Latest blogs

Spotting 8 Days After Embryo Transfer
Spotting 8 days after embryo transfer can worry couples undergoing IVF. It's a crucial moment in...

Spotting 8 Days After Embryo Transfer
Spotting 8 days after embryo transfer can worry couples undergoing...
Life 5 Years after Hysterectomy: Insights & Changes
Life isn't quite the same 5 years after a hysterectomy! It's a...
Day 8 Post IUI No Symptoms
One of the most common fertility treatments is intrauterine...





















